by Rinki Pandey January 7, 2026
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in property management. It is already reshaping how properties are operated, how tenants are supported, and how decisions are made. What once required manual oversight, repetitive follow-ups, and reactive maintenance is increasingly handled through intelligent systems that learn from data and improve over time.
AI in property management is not about replacing people. It is about reducing friction, improving accuracy, and freeing property managers to focus on higher-value work, such as tenant relationships, portfolio strategy, and asset growth. From automated tenant communication to forecasting equipment failures before they happen, AI is quietly becoming a core operational layer in modern property management.
This article explores how AI is being used today, from chatbots to predictive maintenance, and what it means for property managers who want to operate more efficiently, competitively, and responsibly.
Understanding AI in Property Management Operations
Before diving into specific use cases, it’s important to clarify what AI actually means in a property management context. Artificial intelligence refers to software systems that analyze large volumes of data, identify patterns, and make recommendations or take actions without constant human input.
In property management, AI typically works behind the scenes. It analyzes leasing data, maintenance histories, tenant behavior, financial trends, and operational workflows. Based on this data, AI systems help managers anticipate issues, automate routine decisions, and respond faster to changing conditions.
Unlike traditional software, which follows fixed rules, AI systems adapt. For example, an AI-powered platform may notice that certain maintenance issues tend to follow specific warning signs, or that tenant inquiries spike at particular times of day. Over time, the system becomes more accurate and useful.
Importantly, AI in property management is most effective when paired with human oversight. The technology provides insights and automation, while property managers apply judgment, empathy, and local knowledge. This balance ensures that efficiency improves without sacrificing service quality or compliance.
AI Chatbots and Virtual Assistants for Tenant Communication

One of the most visible AI applications in property management is tenant communication through chatbots and virtual assistants. These tools are designed to handle common questions, requests, and updates without requiring staff intervention for every interaction.
Tenants often need quick answers about rent due dates, maintenance request status, parking rules, or move-in procedures. AI chatbots provide instant responses at any time of day, reducing wait times and improving tenant satisfaction. This is especially valuable outside normal business hours, when traditional support is unavailable.
For property managers, chatbots significantly reduce the volume of repetitive inquiries. Instead of answering the same questions repeatedly, staff can focus on more complex or sensitive matters. The chatbot acts as a first point of contact, escalating issues to humans only when needed.
Modern AI chatbots also learn from interactions. If tenants frequently ask about a specific issue, the system improves its responses or proactively provides information. Over time, communication becomes smoother, more consistent, and less resource-intensive.
Crucially, effective chatbot use does not feel robotic. When implemented thoughtfully, AI-driven communication feels helpful and responsive rather than impersonal. The goal is to enhance accessibility, not replace meaningful human engagement.
AI-Driven Leasing and Applicant Screening
Leasing is another area where AI is transforming property management workflows. From managing inquiries to evaluating applicants, AI tools help streamline processes that traditionally required significant manual effort.
AI-powered leasing systems can respond to prospect inquiries instantly, schedule tours automatically, and guide applicants through digital applications. This reduces response delays that often cause prospective tenants to look elsewhere. Faster engagement leads to higher conversion rates and shorter vacancy periods.
In applicant screening, AI assists by analyzing application data consistently and objectively. It helps flag incomplete applications, verify information, and identify patterns that align with established screening criteria. This improves efficiency while supporting fair and consistent decision-making.
For property managers handling high application volumes, AI reduces administrative burden and speeds up leasing timelines. However, human oversight remains essential to ensure compliance with fair housing laws and local regulations. AI supports decisions; it does not replace responsibility.
When used correctly, AI-driven leasing tools create a smoother experience for both applicants and managers, while maintaining transparency and accountability.
Also read: AI-Powered Property Management: Automation and Intelligence in Real Estate Operations
Predictive Maintenance: Moving from Reactive to Proactive Operations
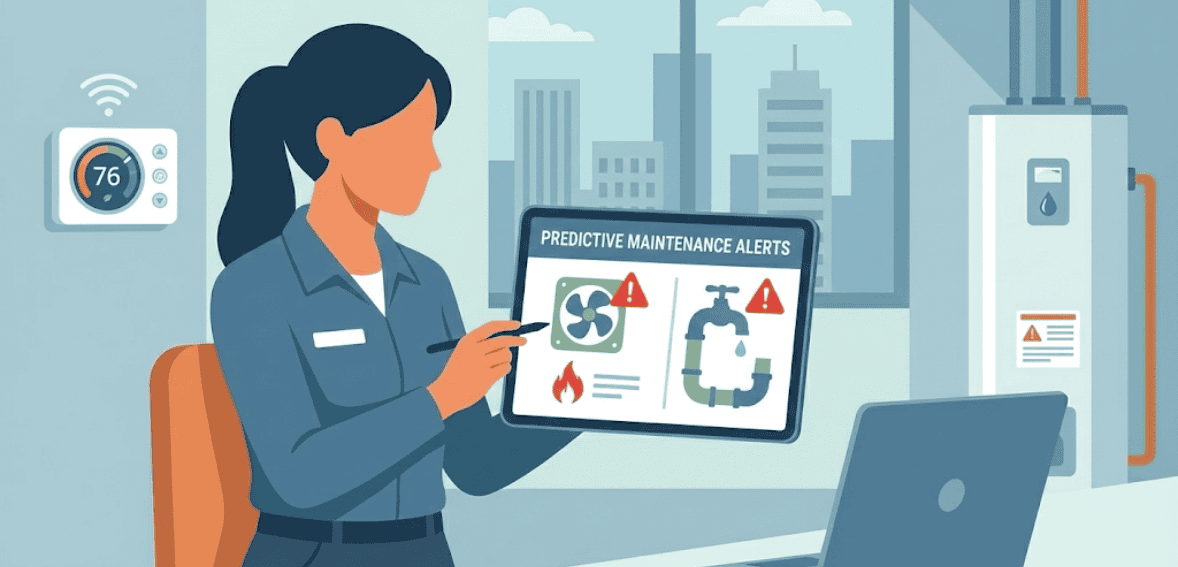
Predictive maintenance represents one of the most impactful uses of AI in property management. Traditionally, maintenance has been reactive, with issues addressed only after something breaks or a tenant complains. AI changes this model by identifying problems before they escalate.
AI systems analyze maintenance records, equipment performance data, sensor readings, and usage patterns. Based on this information, they can predict when systems like HVAC units, elevators, or plumbing components are likely to fail. Property managers receive alerts early, allowing them to schedule repairs proactively.
This approach reduces emergency repairs, minimizes downtime, and lowers long-term maintenance costs. It also improves tenant satisfaction, as residents experience fewer disruptions and faster resolutions.
Predictive maintenance also supports better budgeting and planning. Instead of reacting to unexpected expenses, managers can anticipate costs and allocate resources more effectively. Over time, properties become more reliable, and asset lifespans are extended.
Importantly, predictive maintenance does not eliminate the need for skilled technicians or inspections. It enhances their effectiveness by providing actionable insights that guide decision-making and prioritization.
AI-Powered Rent Optimization and Financial Forecasting
Beyond daily operations, AI in property management plays a powerful role in financial decision-making. One of the most impactful applications is rent optimization using data to set rental prices that balance market demand, occupancy goals, and long-term revenue.
AI systems analyze local market trends, historical leasing data, seasonal demand, vacancy rates, and even economic indicators. Instead of relying solely on intuition or static market comparisons, property managers gain dynamic pricing insights that reflect real-time conditions. This helps avoid underpricing units during high demand or overpricing them during slower periods.
Financial forecasting is another area where AI adds value. Predictive models can estimate future cash flow, anticipate budget shortfalls, and flag properties that may require closer financial attention. For portfolio managers, this provides early visibility into performance trends across multiple assets.
Importantly, AI does not make financial decisions in isolation. It equips managers with clearer insights, enabling them to make informed, strategic choices. This results in more stable revenue, better planning, and improved investor confidence.
Data-Driven Portfolio Insights and Strategic Decision Support
As property portfolios grow, managing them effectively becomes increasingly complex. AI helps cut through this complexity by turning large volumes of operational data into actionable insights.
AI platforms aggregate information from leasing, maintenance, accounting, and tenant interactions into unified dashboards. Patterns that would be difficult to detect manually, such as recurring maintenance issues at specific properties or early warning signs of tenant dissatisfaction, become visible.
This level of insight allows property managers to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive strategy. Decisions about capital improvements, staffing allocation, vendor performance, or asset disposition are supported by data rather than guesswork.
For senior leaders and owners, AI-powered reporting improves transparency. Instead of static reports, they receive forward-looking insights that explain not just what happened, but why it happened and what may happen next. This elevates property management from task execution to strategic asset management.
Ethical, Legal, and Privacy Considerations of AI Use
While AI offers significant benefits, its use in property management also raises important ethical and legal considerations. Tenant data is sensitive, and property managers have a responsibility to protect privacy and ensure fairness.
AI systems must be configured to follow data protection regulations and fair housing laws. For example, screening tools should not introduce bias or discrimination, even unintentionally. Transparency in how AI-driven decisions are made is essential to maintaining trust with tenants and regulators.
Privacy is another key concern. AI platforms often process large amounts of personal and operational data. Property managers must ensure that this data is securely stored, accessed only by authorized users, and used for legitimate purposes.
Responsible AI adoption means setting clear policies, maintaining human oversight, and regularly reviewing system behavior. When managed thoughtfully, AI enhances trust rather than undermining it.
Adopting AI Responsibly in Property Management
Successful AI adoption does not happen overnight. It requires a deliberate approach that aligns technology with operational goals and with the organization’s culture.
Property managers should begin by identifying pain points where AI can deliver immediate value, such as communication bottlenecks, maintenance inefficiencies, or reporting delays. Starting small allows teams to build confidence and refine workflows before expanding AI use.
Training is equally important. Staff must understand how AI tools work, what they can and cannot do, and how to interpret their outputs. AI should be positioned as a support system, not a replacement for human expertise.
Finally, continuous evaluation is critical. AI systems improve over time, but only when monitored and adjusted. Property managers who treat AI as an evolving partner rather than a one-time solution gain the most long-term value.
The Future of AI in Property Management

Looking ahead, AI will continue to deepen its role in property management. Integration with smart building systems, more advanced predictive models, and increasingly personalized tenant experiences are already emerging.
However, the core principle remains unchanged: technology should serve people. The most successful property managers will be those who use AI to enhance efficiency while preserving empathy, accountability, and trust.
AI is not redefining property management by removing the human element; it is redefining it by giving humans better tools to do their jobs well.
Conclusion
AI in property management is no longer optional for forward-thinking operators. From chatbots that improve tenant communication to predictive maintenance that prevents costly failures, artificial intelligence enables smarter, faster, and more resilient operations.
When adopted responsibly, AI reduces administrative burden, improves financial performance, and elevates the tenant experience. The property managers who embrace this evolution thoughtfully will be better positioned to manage complexity, scale sustainably, and remain competitive in a rapidly changing industry.
FAQs
Is AI in property management only for large portfolios?
No. Many AI tools are scalable and can benefit small and mid-sized property managers by automating routine tasks and improving decision-making efficiency.
Does AI replace property managers?
No. AI supports property managers by handling data-heavy and repetitive work, allowing humans to focus on judgment, relationships, and strategy.
Is predictive maintenance expensive to implement?
Costs vary, but predictive maintenance often reduces long-term expenses by preventing major failures and extending equipment life.
How can managers ensure that AI tools follow regulations?
By choosing compliant platforms, maintaining human oversight, and regularly reviewing system outputs for fairness and accuracy.
What is the first step to adopting AI in property management?
Start by identifying operational bottlenecks and implementing AI where it can deliver clear, measurable improvements.